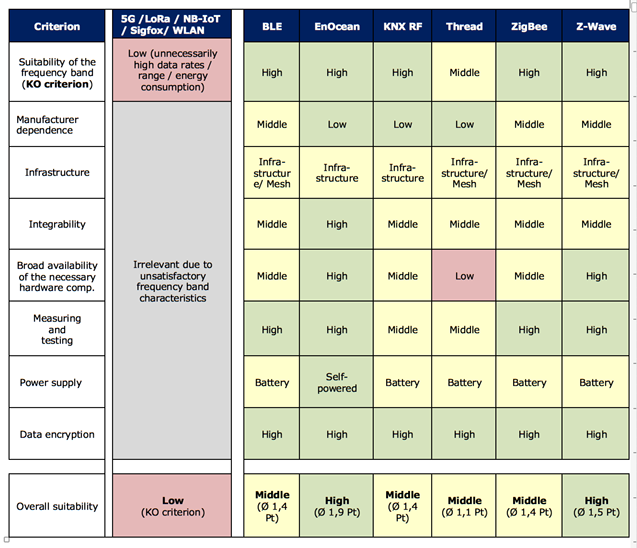
A comparison of wireless standards for building automation and control.
Building automation is on the advance. Systems are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering more and more value-added service features thanks to IT-based systems which surpass what room-/building-management systems could offer until now.
These systems are heavily reliant upon data from within spaces and buildings, which can easily be gathered and transmitted by means of wireless technology. Various wireless standards are available, including LoRa, Bluetooth Low Energy, Sigfox, EnOcean, Z-Wave, ZigBee. A study [1] by Prof. Dr. Michael Krödel (IGT – Institut für Gebäudetechnik/Institute for Building Technology) now points out which of these are suitable for use in smart buildings.
The most suitable wireless technology can only be identified, case by case, according to the specific application and the ‘use cases’.
In this context it has become apparent that the so-called ‘Wide Area Networks’ are unsuitable for today’s and tomorrow’s Smart Building applications. This technology is well suited to integrating wireless devices into public areas, i.e. where it is impossible to establish one’s own infrastructure. In modern buildings, however, setting up an own infrastructure or establishing mesh networks presents no problems and makes excellent sense in consideration of the density of the sensor networks.
Other wireless technologies are more – or less – suited to this kind of application. The possibility of integrating wireless devices (especially sensors) into building automation systems – e.g. controllers and DDC-systems – is of particular relevance. The support for specific wireless technologies offered by controller manufacturers plays an important role. As does the possibility of sourcing a broad range of compatible components on the open market. Not to mention the great advantages offered by self-powered wireless devices requiring neither batteries nor mains power.
From these points of view, the EnOcean and Z-Wave wireless standards appear to be ideal for use in ‘Smart Buildings’. EnOcean achieved a mean score of 1.9 points on the suitability index followed by Z-Wave with 1.5 points.
However, these technologies cater for different market segments. EnOcean is predestined for use in professionally-installed integrated systems for Smart Home and non-residential building solutions and features higher levels of interoperability. In contrast, Z-Wave is better suited to ‘DIY’ Smart Home consumer-level retrofit applications.

Use Cases in modern buildings
The foreseeable Use Cases form the basis for the evaluation of the suitability of different wireless data transmission standards. One must first define what needs to be automated in order to evaluate the best solution amongst the various wireless standards available.
Typical room-/building-automation Use Cases include:
- Individual room temperature regulation according to human presence and window status.
- Individual room ventilation and cooling depending on air temperature, air quality (CO2 and/or VOC loads) and humidity.
- Individual room lighting – illumination can be dimmed when areas are not in use. Switches can govern individual lights or groups of lights as needed. Artificial light intensity can also vary according to natural light intensity depending on the weather and time of day.
- Sunblinds/shutters can be deployed automatically in function of room temperature (summertime heat protection).
- Switches for illumination and external light shading can be optimally placed, with the free positioning of furniture and partitions/walls. Handheld remote-controls can also be employed.
- The supply of warmth for heating systems or refrigeration for cooling systems can be regulated to match current and projected system demands (including criteria for flow temperatures and pump rotation speed regulation).
- Multiple heat/cold-generating units can be governed according to system performance requirements and loads
- Heat regeneration for ventilation systems can be configured to avoid icing or overheating.
- Fault alarms, operating hours and energy consumption can be protocolled and evaluated.
Further value-added services currently seeing intensive development include:
- The smartphone-based dynamic booking/release of conference-room facilities and workplaces in open-plan offices. Meetings finishing ahead of schedule and unoccupied workplaces can be recognized and taken into account for optimal facility management.
- Occupancy sensors can, for instance, be used to analyse the use of meeting rooms, recognize resource usage patterns, protocol no-shows, manage workspace efficiently and organize catering services.
- The analysis of usage patterns enables the flexible allocation of employee workspace. Unutilized areas can be set to energy-saving mode, thereby cutting heating/cooling/electric power costs.
- Building occupancy can be displayed graphically by employing ‘Heat Maps’ or ‘Moving Trails’ illustrating how many persons are occupying which areas.
- Such insight provides the perfect basis for zone planning purposes (e.g. room size, position of meeting rooms etc.).
- Employees and visitors can be easily guided through the building complex, making orienteering simpler in unfamiliar facilities e.g. when looking for a specific meeting room
- Canteen usage (i.e. foreseeable waiting times) can be monitored and visualised from the workplace.
- The frequency of washroom usage can be monitored and translated into appropriate cleaning schedules.
- Usage of lifts, coffee machines etc. can be monitored and translated into adequate maintenance schedules.
- Sensors within the building automation network monitor pumps, cleaning machines, HVAC systems, lifts etc. and report any malfunction in real time for better fault-finding and more efficient pre-emptive measures.
Parameters for the analysis of wireless standard suitability for automation and control
The Use Cases enable us to make accurate assumptions concerning the suitability of individual wireless standards. These are the relevant criteria:
- Suitability of the frequency band (KO-criterion): the Use Cases typically feature small data packets (10-100 bytes), latency times from 0.1 second to 1 second and a range from 10 to 100 metres. The suitability of the frequency band is of decisive importance – any functional limitation, even if partial, would essentially disqualify the wireless standard in question for this type of application.
- Manufacturer dependence: in the best interests of the user, wireless standards should operate across as many suppliers as possible. Wireless technology should be standardised in order to allow for maximal interoperability between devices produced by different suppliers.
- Infrastructure: ideally, an own infrastructure should not be required. This is a given when signals can be transmitted over greater distances and is particularly relevant when sensor network density is low. In return, an infrastructure consisting of cable-connected antennas and gateways allowing for meshed communication is required.
- Integrability: ideally, wireless standards should be broadly supported by multiple manufacturers of commercially-available controllers and gateways, with proven reference project information.
- Broad availability of the necessary hardware components: all the necessary sensors must be freely available on the open market.
- Measuring and testing: the appropriate fault-finding equipment and user documentation must be available.
- Power supply: one of the main advantages of wireless technology consists of the free positioning of sensor devices. A cabled power supply represents a hindrance. Ideally, sensors should be self-powered. For battery-powered devices, a low power consumption is of great importance.
- Data encryption: data security and integrity must be guaranteed by encryption technology
Wireless standard suitability for building automation and control
The table at the head of this page shows a comprehensive comparison. Details can be found in the study mentioned below.
[1] ‘Smart Building’ trends – a comparison between various wireless standards; IGT – Institute for Building Technology/Institut für Gebäudetechnologie; 2020
To download the full white paper, please follow this link: https://www.enocean-alliance.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/04/Wireless-Standards-for-Smart-Buildings.pdf
About EnOcean Alliance
The EnOcean Alliance is an international association of leading companies in the building and IT industries founded in 2008. The open, non-profit organization is committed to enabling and promoting interoperable, maintenance-free and proven eco-systems based on the wireless EnOcean radio standard (ISO/IEC 14543-3-10/11). With their decades of experience EnOcean Alliance members strive to co-create a healthy, safe and sustainable environment in smart homes, intelligent buildings and smart spaces for the benefit of all. The EnOcean Alliance headquarters are located in San Ramon, California.
Related Articles
Nordic-powered module provides Bluetooth LE Audio connectivity for headphones, speakers & audio systems
Rayson Technology’s BTM-N340X employs nRF5340 SoC for LE Audio plus advanced metering and home automation applications Wireless communications company Rayson Technology has released a multiprotocol module based on Nordic Semiconductor’s nRF5340 System-on-Chip (SoC)....

Anritsu, Sony Semiconductor validate industry first Non-Terrestrial Network (NTN) NB-IoT testcase
First NTN NB-IoT Protocol Conformance Tests for have been validated on the 5G NR Mobile Test Device Platform Anritsu Corporation has announced that the first NTN NB-IoT Protocol Conformance Tests for has been validated on the 5G NR Mobile Device Test Platform ME7834NR...
Ellisys Introduces Support for CCC Digital Key Technology
Protocol Updates Aid in Test, Validation, and Debug for Automotive and Consumer Electronics Developers and Test Labs Ellisys, a leading worldwide provider of Bluetooth®, Universal Serial Bus (USB), Ultra-Wideband, and Wi-Fi® protocol test and analysis solutions has...
1 Comment
Stay Up to Date With The Latest News & Updates
Our Sponsors
Incisor.TV partners with leading organisations in the technology sector.
Follow Us
And stay up to date with our news! We are active across the key social media platforms – please do follow us!





Reading this article I was wondering how the table would be looking if ULE (Ultra Low Energy) was included. ULE, with dedicated, interference free frequency, communication range almost 10 times longer than any other technology in the table, with ability to deliver voice and video (in fact, the only short range wireless technology with guaranteed voice quality!). ULE is in use by world’s leading companies, (a short list: Deutsche TEleCOM, ORange, Panasonic, Vtech, Gigaset and recently ADT – USA’s leading security company).
Selection of comparison criteria is a tricky subject, as one can select criterion that “works best for the final goal”. For example, One can claim that data bandwidth is not important because you need only few bits of information traffic from/to the sensors; others may claim that this is archaic approach, not relevant anymore for 21st century technologies, and that the best suitable technology would be versatile, which can operate on a very low power when “everything is quiet”, but can provide the necessary information in case of real emergency via voice, video or just data – this is ULE’s unique capability, that makes it the most suitable technology for the building automation.